I am interested in this product
Close Form
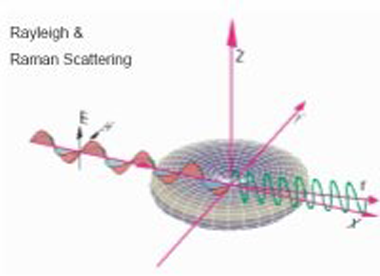
An elastic scattering process where the scattering particles are small compared to the wavelength of the incident light is called Rayleigh Scattering (RS).
I am interested in this product
Close Form
Downloads
Detailed Specs
That is the case for gas phase molecules and, therefore, this method is suited for laser imaging in gases. RS leads to images containing weighted information about the total gas density. It occurs from all constituent molecules. The scattered light is almost at the same wavelength as the incident light. Its use requires either constant gas composition or known mole fractions of all major species. When gas composition and pressure are known Rayleigh imaging allows to measure planar temperature fields (Rayleigh Thermometry). Rayleigh scattering is much weaker than Mie scattering but more than two orders of magnitude stronger than Spontaneous Raman Scattering (SRS). Incandescence from soot and Mie scattering are processes that can totally obscure the Rayleigh signal.


